2019
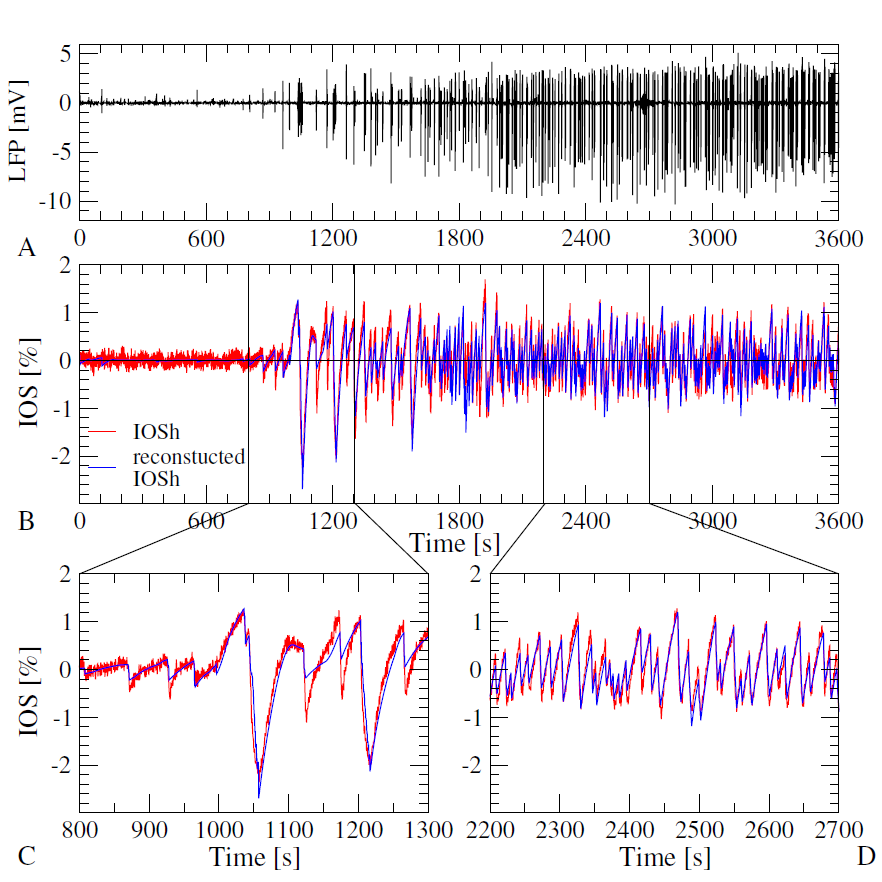
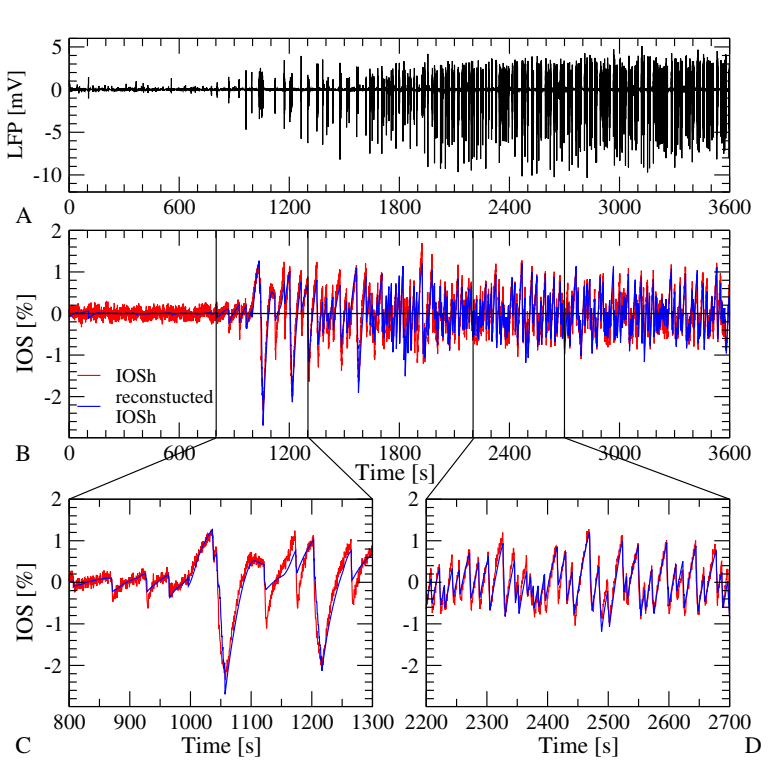
Figure 1. Reconstruction of the Intrinsic Optical Signal (IOSh) based on the measured Local Field Potential (LFP). A: The temporal evolution of the LFP during evoked epileptic activity of the brain slice. B-D: Comparison of the measured (red) and the reconstrucetd IOSh signal (blue). The reconstruction follows the measurement through different dynamic regimes.
Causality analysis between electrical signals of neural activity and the intrinsic optical signal of the neural tissue. — Causal relationship between local field potential (LFP) and intrinsic optical signal (IOS) in evoked epileptiform activity in vitro brain slices was investigated. The parallel IOS and LFP recordings were performed by Sándor Borbély and Ildikó Világi (Eötvös Loránd University). As far as we know, this work was the first conclusive application of the Sugihara’s new causality method, the cross-convergent mapping (CCM) in neuroscience. As CCM is the first causality analysis method which can reliably detect the circular connection, we were in the position of investigating the question, whether only the evoked epileptic activity causes the intrinsic optical signal IOS, or there is a feedback mechanism as well, and the ion concentration changes measured by the IOS influence the termination or the renewal of the epileptic activity.During preprocessing, two components of the IOS signal have been distinguished: a faster, activity dependent component (IOSh) which changes its sign between transmitted and reflected light measurements thus it is related to the reflectance or the dispersion of the tissue and a slower component (IOSl), which is negative in both cases, thus can be attributed to the increase of the absorption of the tissue. We found only unidirectional causal drive from the electric towards the optical signal, but this work demonstrated several phenomena which are instructive for further investigation: We found, that the correlation was small between the LFP and the IOSh at the time of the actual causal effect and the peaks of the cross correlation function did not reflect the actual causal dependency in this case. In stead, the temporal derivative of the IOSh was correlated with the LFP power at the time delay of the causal peak. Based on these observations, a simple model have been set up to describe the dependency of the IOSh on the LFP power and IOSh was reconstructed, based on the LFP signal (Fig. 1.). Besides the actual results, we believe that this study demonstrates, that it is possible to calculate the causality between two data series with drastically different time scales and provides useful know-how for application of causality analysis for any field of science [1].
Emergence of polarized opinions from free association networks. — We developed a method that can identify polarized public opinions by finding modules in a network of statistically related free word associations. Associations to the cue “migrant” were collected from two independent and comprehensive samples in Hungary (N1 = 505, N2 = 505). The co-occurrence-based relations of the free word associations reflected emotional similarity, and the modules of the association network were validated with well-established measures. The positive pole of the associations was gathered around the concept of “Refugees” who need help, whereas the negative pole associated asylum seekers with “Violence” (Fig. 2). The results were relatively consistent in the two independent samples. We demonstrated that analyzing the modular organization of association networks can be a tool for identifying the most important dimensions of public opinion about a relevant social issue without using predefined constructs) [2].



