2017
The year 2017 has concluded the “Momentum” grant support of the group from the HAS, which will continue as a permanent funding. The key focus of the group was the completion of the already existing commitments. This includes contributions to specific CERN experiments, such as the ALICE, NA61 and RD51. Detector physics projects and neutron detector development were financed by H2020 grants. Using detectors developed by the group, an active volcano imaging has been performed in collaboration with Tokyo University and the NEC company.
Contributions to CERN Collaborations. — The activities of the group in the Time Projection Chamber (TPC) Upgrade Collaboration has reached nearly half way, with about 200 large size gas electron multiplier (GEM) foils processed in Budapest. The Advanced Quality Assurance testing site which was established, is the second step of the TPC construction after production (at CERN), and the foils are forwarded to Germany and the USA. Within the framework of the NA61 Collaboration, three new TPC-s were built and installed to capture the forward particles.
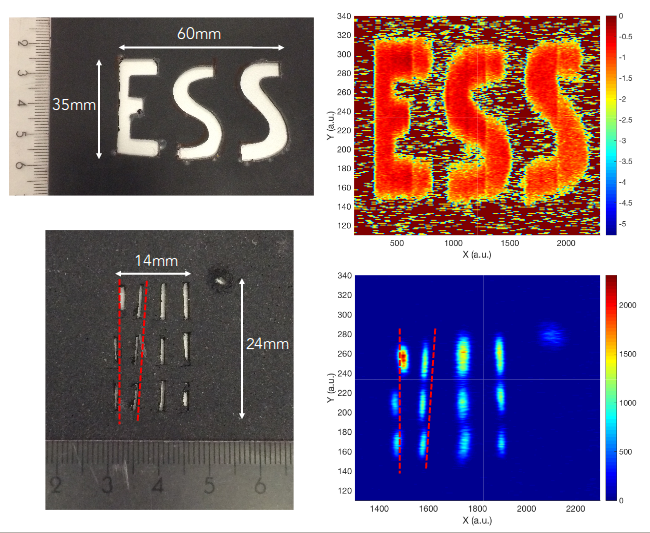
Figure 1. Images taken with the Multi-Blade detector, using neutrons at the Budapest Neutron Center. Precise and high contrast images have been recorded, consistently with the design goal for neutron reflectometry at ESS.
Imaging with cosmic muons. — The application of cosmic muons for large scale imaging has been a research direction in the group in the previous years. An important application for cosmic muons detectors, developed in the last years by the group, is imaging the interior of volcanos. This direction was pursued by Japanese and various European groups. Gaseous tracking detectors, and in our case, a specific type of a multi-wire proportional chamber (MWPC) developed by our group, are highly competitive with the traditional scintillators in terms of cost, weight and power consumption. A utility patent has been filed in Japan, owned jointly by Wigner RCP and Tokyo University, for the so-called “Muography Observation System” (MOS). The detector system has been installed by the Sakurajima volcano in Japan (southern island), to demonstrate the true applicability and sufficiently low level of background, and to gain experience for the future developments. Presently 1.2 square meter sensitive area is installed, which will increase in the coming years. The japanese NEC company, which has licensed the MOS for research purposes, has started a cooperation with the patent owners to understand the market needs for muography.Multi-Blade detector demonstrator for ESS. — The high intensity, high position resolution neutron detector, called the Multi-Blade, has been tested with cold neutron beam at the Budapest Neutron Center. The results show that the position resolution, below 0.5mm in one direction, is indeed reached. Other testing has clarified the intensity tolerance of the design, which, by the delicate interplay between geometry and detection mechanism, is higher than most other competing versions. Demonstration images are shown in Fig. 1.
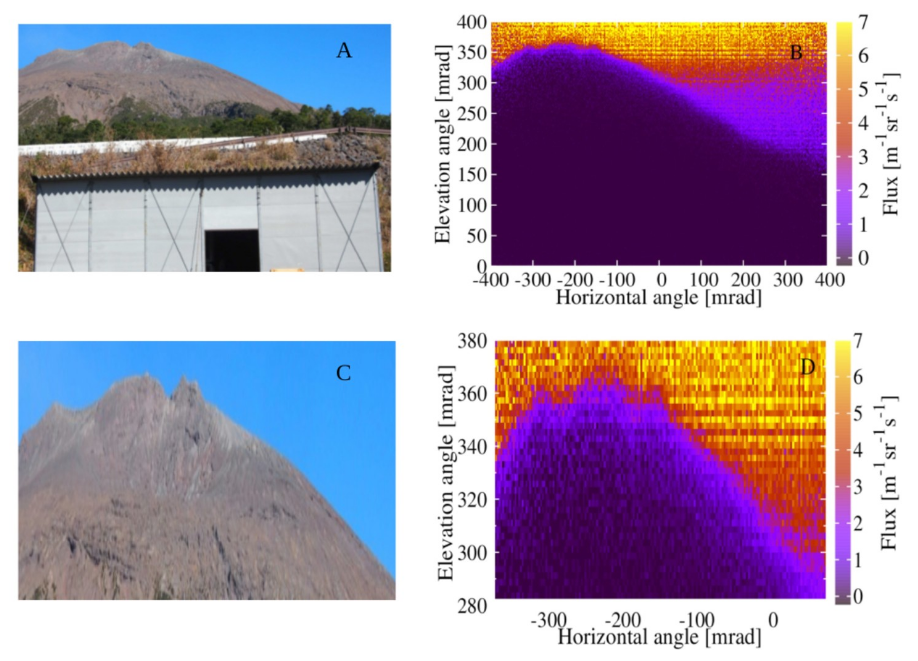
Figure 2. Visual (left) and muographic (right) images of the Sakurajima volcano in Kyushu (Japan), taken with the MOS. The detectors were developed at Wigner RCP, installed in a structure designed and constructed by Tokyo University.



