2023
Investigation of the coordination of human lower and upper limb movements from various aspects
This year, we focused on the simultaneous cyclic movements of the human arm and leg. In cyclic movements, there is an interaction between the upper and lower limbs, for example in walking or in swimming. The cycling task is well known and widely used in the rehabilitation of people with movement disorders, so we focused on this task.
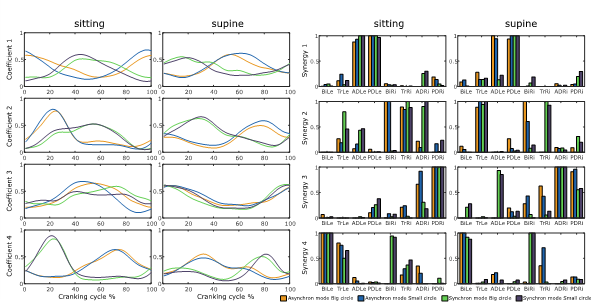
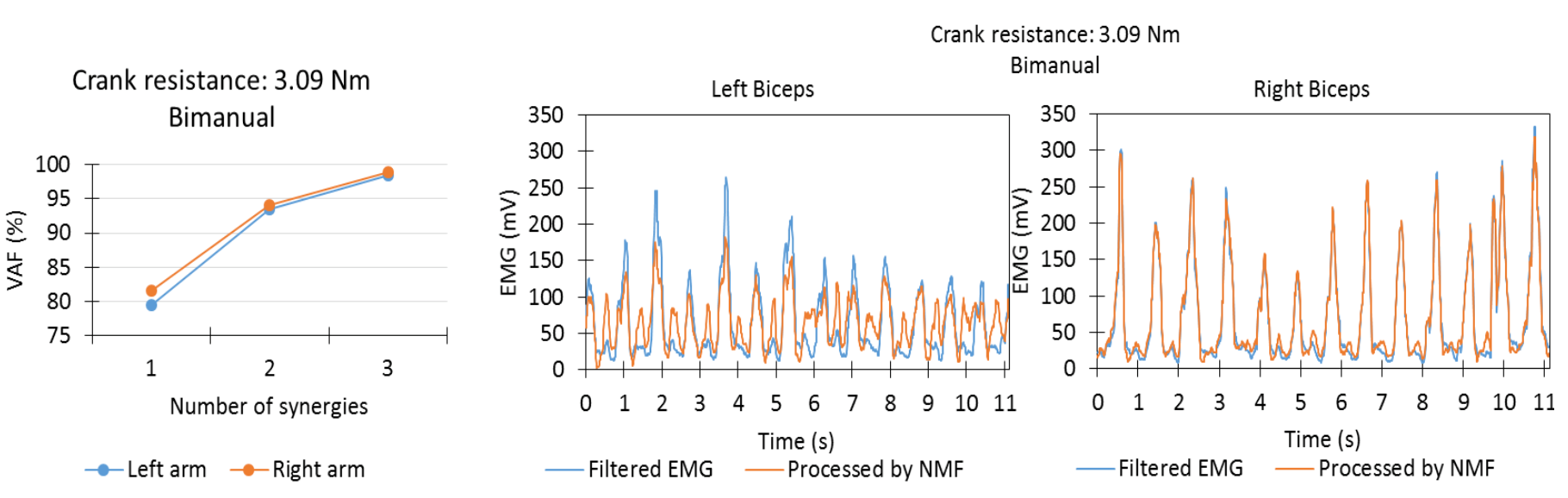
Muscle synergies in simultaneous arm and leg cycling task. — In the first project, the healthy participants performed the leg cycling and the arm cranking task simultaneously on an arm-leg cycle ergometer. The kinematic data of the body and the muscle activity data with EMG were measured. We investigated the muscle coordination, in terms of muscle synergies by the non-negative matrix factorization algorithm in the different cycling conditions. Interlimb muscle synergies were represented by synergy vectors, explored during the simultaneous arm and leg cycling in a case study [1]. We found that 6 synergy vectors were sufficient to reconstruct 12 muscle’s original (measured) activity.

Figure 1. Interlimb synergies between arm and leg muscles in 2 different crank resistance conditions.
Further question is, whether leg cycling has an effect on arm cycling at the level of muscle synergies? We compared the arm muscle synergies when participants performed the cycling simultaneously with arms and legs to that case in which cycling was performed only with the arms. We are working on a manuscript on this topic with our Spanish colleagues.
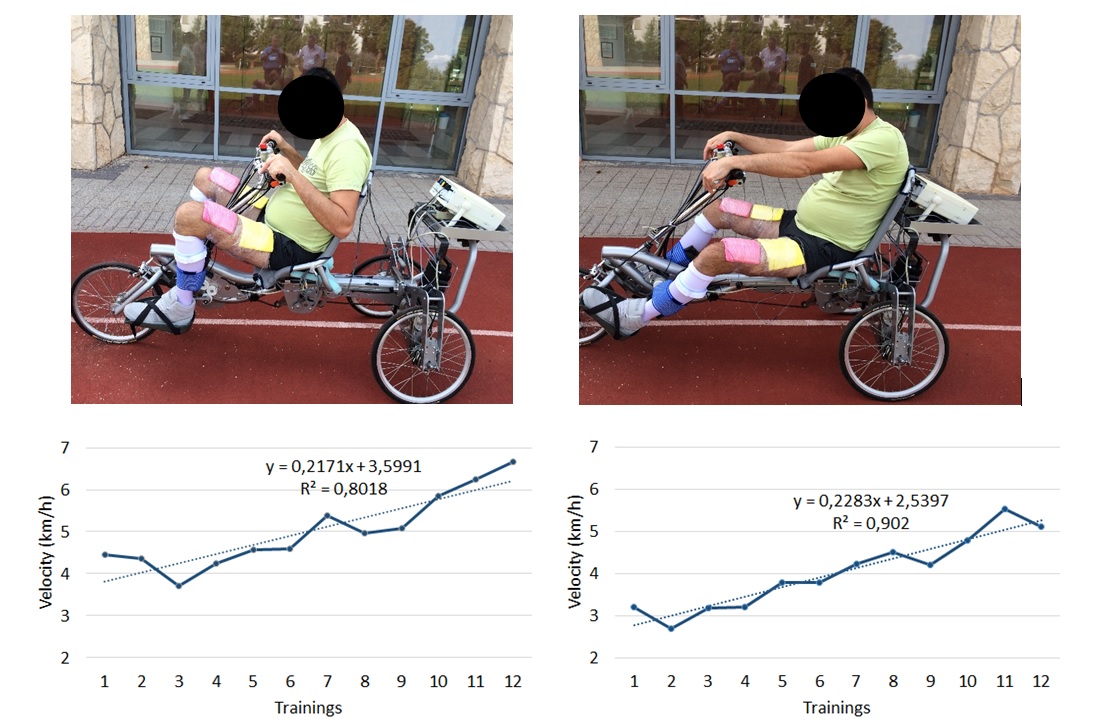
Effect of the hybrid FES cycling therapy on gait parameters of incomplete spinal cord injured patients. — The other main topic is the investigation of the role of the arm in functional electrical stimulation (FES) assisted cycling therapy. During the FES therapy the paralized muscles are electrically stimulated to perform a predefined task. During the hybrid FES, the FES assisted leg cycling are supplemented with voluntary arm cranking. In our study we work together with colleagues from the National Institute for Medical Rehabilitation. The improvement of walking ability of incomplete spinal cord injured patients is examined in response to hybrid FES cycling therapy. The patients take part a 12 week long rehabilitation training program, they have hybrid FES cycling therapy twice a week, and we measure gait parameters and gait dynamics before the start of the training, then in every third week and finally at the end of the training. The processed data show that walking ability improved, that is reflected in gait parameters, e.g. in the length of center of pressure that acts on the body during walking [2]. Our first case study has been accepted in the “Rehabilitáció” journal [3] ,
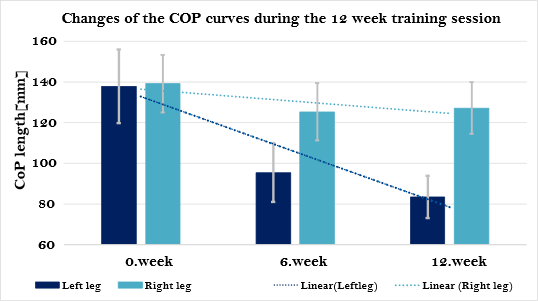
Figure 2. Decreasing of the lengths of the Center of Pressure curves during the training sessions. This suggests that the gait stability has improved as a result of the rehabilitation therapy.
References:
[1] Botzheim L., Radeleczki B., Mravcsik M., Barroso F.O.,Laczko J., Investigation of Muscle Synergies during Simultaneous ARM-LEG cycling – Case Study. In: Progress in Motor Control XIV : Abstract Book, p51. Ambino Gesù Children Hospital (2023) p. 75
[2] B. Radeleczki, L. Botzheim, N. Nagy, J. Laczkó, and M. Mravcsik, “Change of ground reaction force and center of pressure in walking of spinal cord injured patients after FES cycling training – case studies.,” in Progress in Clinical Motor Control - Neurorehabilitation II., Program Abstracts, 2023, p. 120.
[3] B. Radeleczki, N. Nagy, M. Mravcsik, P.Szemerédi, M. Futó, L Ware, M. Fehér, A. Klauber, P. Cserháti, J. Laczkó, L. Botzheim. “A hibrid FES kerékpározó terápia szerepe részleges gerincvelősérültek rehabilitációjában – esettanulmány “ accepted in Rehabilitáció Journal, 2023.